Security Headers
What are security headers?
Security headers are HTTP headers which are set in the responses sent from the origin server to the visitor. These headers define the behaviour of the browser when viewing the webpage and help to prevent common attacks such as Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), Click jacking, or code injection.
Polaris simplifies the configuration of these HTTP headers by letting you choose which settings you would like and handling the technical implementation automatically.
Accessing Security Headers in Polaris
Click on Settings of your site.
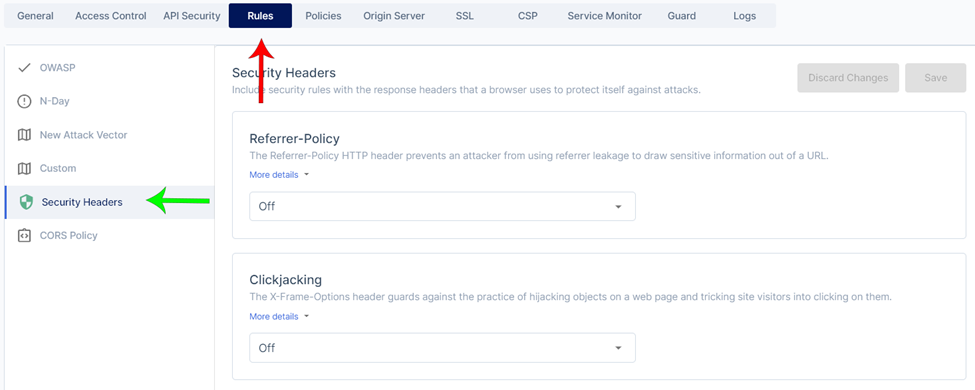
Click on Rules (red arrow) then Security Headers (green arrow) to access it.
What headers can you set with Polaris?
Polaris helps to configure several security headers. Each of them help against a specific type of attack, however they can also cause problems with the functionality of the website in some cases. Please ensure that your webpage is able to function as intended with the settings in place. The following are the security headers Polaris helps configure:
Referrer Policy
When a browser goes from one page to another, it includes the address of its originating page in a HTTP header called the referrer. This occurs even when the browser goes to another domain, possibly leaking information of the referrer to an untrustworthy domain. To prevent this, you can use the Referrer-Policy HTTP header to declare your website's policy on withholding referrer information. The options for this setting are as follows:
Off: The Referrer header will be omitted entirely. No referrer information is sent along with requests.No referrer: The Referrer header will be omitted entirely. No referrer information is sent along with requests.No referrer when downgrade: Send the origin, path, and query string in the Referrer header when the protocol security level stays the same or improves. Don't send the Referrer header for requests to less secure destinations.Origin: Send only the origin in the Referrer header, i.e. when the Referrer is example.com/example1/example2 only example.com will be sent.Origin when cross origin: Send the origin, path, and query string when performing a same-origin request to the same protocol level. Send only the origin for cross-origin requests and requests to less secure destinations. Cross-origin requests occur when the browser brings you to a website from a different origin.Same origin: Send the origin, path, and query string for same-origin requests. Doesn't send the Referrer header for cross-origin requests.Strict origin: Send only the origin when the protocol security level stays the same. Doesn't send the Referrer header to less secure destinations.Strict origin when cross origin(default): Send the origin, path and query string when performing a same origin request. For cross-origin requests send only the origin when the protocol level stays the same. Doesn't send the Referrer header to less secure designations.Unsafe url: Send the origin, path, and query string when performing any request, regardless of security.
Click Jacking
Polaris protects against click jacking by implementing the X-Frame-Options header. This prevents attackers from hijacking objects on your website and tricking visitors into clicking them. The options available are as follows:
Off: Tiêu đề không được thiết lậpNo content within frame: The page cannot be displayed in a frame, regardless of the site attempting to do so.Allow content within frame from same origin: The page can only be displayed in a frame on the same origin as the page itself. The exact implementation of this differs from browser to browser.Allow content within frame from specific origin: A page can be displayed in a frame only on the specified origin URL.
XSS (Cross Site Scripting)
An attacker uses XSS to inject malicious content into a request between the browser and the origin server. A server may execute the malicious script if it does not sanitise the HTML query parameters. Polaris uses the X-XSS-Protection header to prevent this from occurring. The options available for this header are as follows:
Off: Disables XSS filtering.Sanitise script: Enables XSS filtering. If a cross-site scripting attack is detected, the browser will sanitise the page by removing the unsafe parts.Block script: Enables XSS filtering. Rather than sanitising the page, the browser will prevent the rendering of the page if an attack is detected.
Mime Sniffing
To guard against arbitrary uploads to your webpage, Polaris uses the X-Content-Type-Options header. This disables the browser's MIME sniffing capabilities and demands that a browser uses the original MIME type of a file as defined by its source. The options available for this header are:
Off: Header is not set.No sniff: Blocks a request if the request destination is of typestyleand the MIME type is nottext/css, or if it is of typescriptand the MIME type is not a JavaScript MIME type. It enables Cross-Origin Read Blocking (CORB) protection for the following MIME types:a. text / html
b. text / plain
c. text / json
d. application / json or any other type with a JSON extension: * / * + json
e. text / xml, application / xml or any other type with an XML extension: * / * + xml (excluding image / svg + xml)
Security Headers Preview
At the bottom of the Security Headers tab, you will be able to see the overview of all the security headers which will be applied to the responses from your origin server.
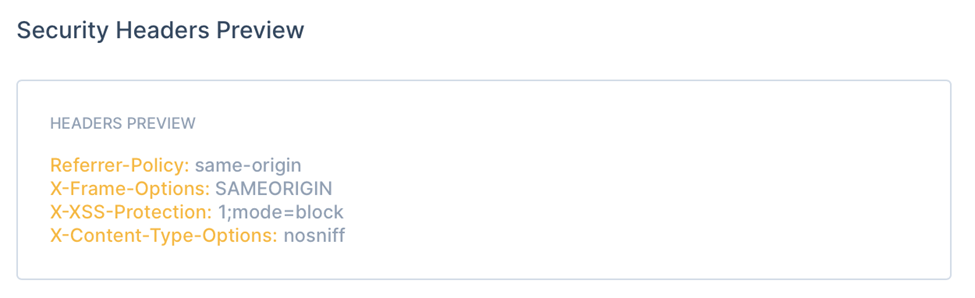 Overview of Security Headers
Overview of Security Headers