API Security
Why are APIs Important?
API endpoints are the points through which APIs (Application Programming Interface) communicate with site visitors. APIs serve as the connections between different platforms and systems, allowing them to share information and resources. An example of this is an e-commerce web application that integrates with a financial payment gateway platform to enable online payments by customers. The APIs allow the e-commerce platform to "talk" to the payment platform.
APIs are important for defense because they can be exploited to gain entry into your network or manipulated to steal confidential data. Some specific security concerns with APIs include:
API Keys - These allow for a unique connection to be made between two parties and should be private. It is usually provisioned by a service provider to a partner who uses their services. These API Keys can be stolen and used to do things such as impersonate a client.
Usernames/Passwords - Oftentimes, API requests utilize your confidential login information as it provisions authentication and authorization for the use of services. Like in the previous example, a user may use an e-commerce site and pay online via a payment gateway. That payment gateway more often than not will require a login so that you can access historical payments, credit card information etc. This confidential data may be sent from one system to another in order to allow you to complete your transaction.
3rd Party Authentication services - Services like Google and Microsoft Azure allow for single-sign on access (SSO), so that users can use their already existing login information to access a web application. These 3rd parties provide OAuth services, provisioning of an authentication token to prove you are who you say you are. If the OAuth is compromised in an API attack, the results are much like losing your username and password. Attackers can then use those compromised credentials for attacks or unauthorized access.
API Defense
APIs are important for defense because they can be exploited to gain entry into your network or manipulated to steal confidential data. Some specific security concerns with APIs include:
So how does the Polaris WAAP defend against API attacks? Much like other attacks, once API endpoints are added to our platform, we're able to monitor the API request traffic to ensure it looks and behaves the way it should.
Next Generation Web Application Firewall (NGWAF) - our AI/ML firewall filters traffic based on standard default rulesets or customized rules set by the platform user. These rules allow for the acceptance or blocking of API requests based on known signatures or behavior. Intelligent behavior learning features allow traffic to be analyzed and corroborated to determine more complex attack patterns, as well as newer possible Zero Day attacks.
Schema Validation - the NGWAF also more specifically checks API requests and responses to determine if they match expected behavior as outlined. When adding OpenAPI Specs to the WAAP, the user can see expected requests and responses of their API are clearly outlined. Anything out of the spectrum provided will be analyzed for maliciousness.
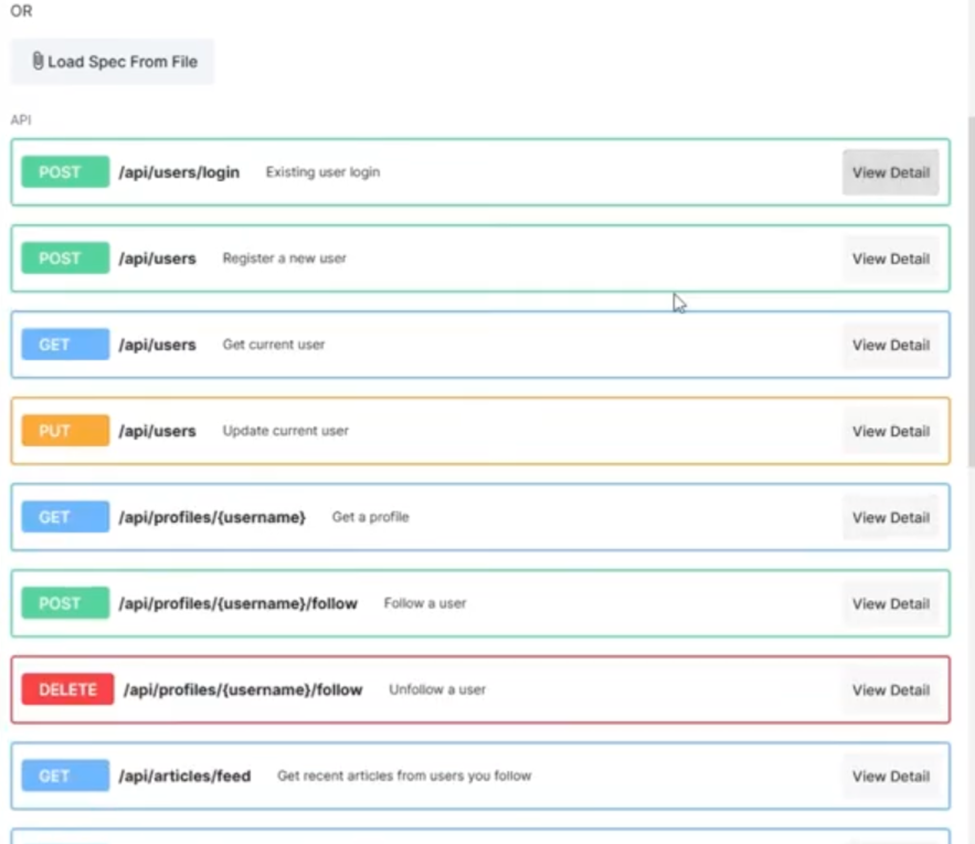 Listed behaviors and expected responses for an API endpoint as displayed in the WAAP
Listed behaviors and expected responses for an API endpoint as displayed in the WAAP
Risks of Failure
APIs are a growing risk because more often than not, people don't think about securing them. Other times, there may be so many or people don't know they have APIs. The risk of failure include:
- Authentication Attacks - provisions an attacker access to your network through methods such as stolen credentials and using credential stuffing.
- Authorization Attacks - once in a network, allows an attacker to take certain actions due to escalated privileges or move to specific areas within a network in which they should not be allowed.
- DDoS - slowing or halting web application functions because too many API requests are sent, flooding systems.
- Vulnerability Attacks - - flaws in the API itself or the web application's integration of the API that allow for more targeted attacks using customized or OWASP Top 10 attacks such as Remote Code Execution (RCE).